Seata TCC Mode
Review the description in the overview: A distributed global transaction, the whole is a two-phase commit model. The global transaction is composed of several branch transactions. The branch transaction must meet the requirements of the two-phase commit model, that is, each branch transaction must have its own:
- One-stage prepare behavior
- Two-phase commit or rollback behavior
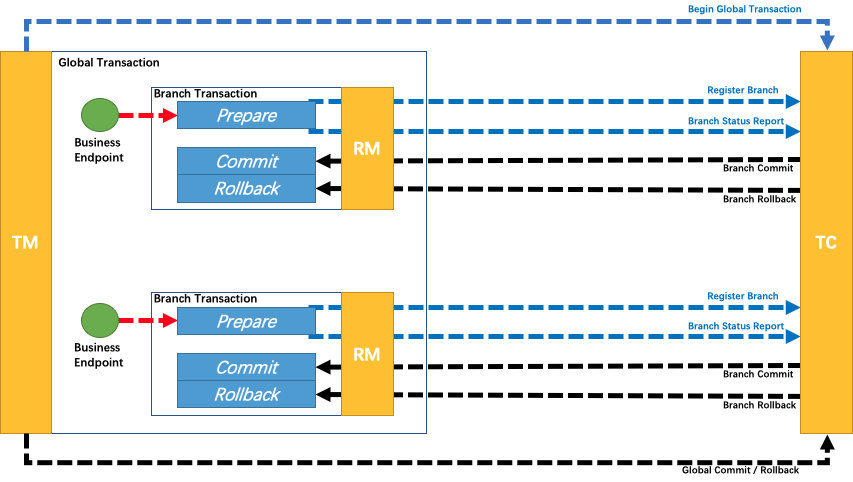
According to the two-phase behavior mode, we divide branch transactions into Automatic (Branch) Transaction Mode and TCC (Branch) Transaction Mode.
The AT mode (Reference Link TBD) is based on a relational database that supports local ACID transactions:
- One-stage prepare behavior: In local transactions, business data updates and corresponding rollback log records are submitted together.
- Two-phase commit behavior: Immediately completed successfully, automatically asynchronously clean up the rollback log.
- Two-phase rollback behavior: Through the rollback log, automatically generates compensation operations to complete data rollback.
Correspondingly, the TCC mode does not rely on transaction support of the underlying data resources:
- One-stage prepare behavior: Call the custom prepare logic.
- Two-phase commit behavior: Call custom commit logic.
- Two-phase rollback behavior: Call the custom rollback logic.
The so-called TCC mode refers to the support of putting customized's branch transactions into the management of global transactions.